Glossary

Gait
The pattern of movement of animals during (terrestrial) locomotion.
Gaits used by cats and dogs include the walk, the amble, the pace, the trot, the canter and the gallop.
Gaits used by cats and dogs include the walk, the amble, the pace, the trot, the canter and the gallop.
Fault
A characteristic of a pet that deviates from the breed standard.
Breed standards specify characteristics that are undesirable, some being disqualifying faults.
Breed standards specify characteristics that are undesirable, some being disqualifying faults.
Trot
A symmetrical, two-beat gait in which diagonally contralateral limbs move in unison.
This is an endurance gait, which allows coverage of ground at a reasonable speed but without expending maximum energy. The trot may, therefore, be maintained for hours.
This is an endurance gait, which allows coverage of ground at a reasonable speed but without expending maximum energy. The trot may, therefore, be maintained for hours.
Forefoot
The foot of a cranial (anterior) limb.
Central Line
An imaginary line along the direction of travel.


Stifle
The region or joint between the femur (upper thigh) bone and the tibia and fibula (lower thigh) bones.
Equivalent to the human knee.
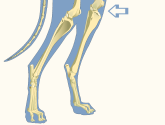
Equivalent to the human knee.

Spread Hocks
A fault of gait in which hock joints twist outwards.
This causes the feet to toe in.
This causes the feet to toe in.
Foot
The distal part of a limb that bears weight, and facilitates locomotion and manipulation.


Hock
The tarsal region or tarsal joint of the hind leg of a quadruped.
Also known (colloquially) as the heel or ankle.
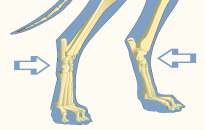
Also known (colloquially) as the heel or ankle.







